If you are thinking about starting a multilingual SEM campaign, you will need to prepare yourself much more than you would for any domestic marketing campaign you’ve done.
Everything from technical SEM to the process of keyword selection and copywriting needs to be considered within the framework of the new country in which you will be marketing.
In this chapter, I will go over the essential points to remember when conducting multilingual SEM so that you can start your venture off on the right path.
Fundamentals of Multilingual PPC Advertising
PPC advertising, or paid search, is a great form of online advertising to choose if you are considering marketing in foreign countries.
Its foremost merit is that it makes reaching potential consumers easy and effective through the use of search engines as an advertising medium.
As most of the online community across the world uses search engines on a regular basis, the reach that you can obtain via PPC advertising is significantly higher compared to other advertising platforms.
Global paid search involves many languages, though, so if you want to reach consumers across the world, simple, direct keyword and ad copy translations will not suffice.
This is one of the challenges you will face. Another challenge is that in other countries, there are unique paid search advertising platforms (e.g. Baidu in China, Naver in South Korea, and Yandex in Russia) that you will have to learn how to operate.
In this chapter, I will provide you the know-how needed in order to conduct multilingual, global PPC campaigns effectively. That way, it will be a fun, not stressful, experience.
Different Countries, Different Search Engines
The first step in starting a global paid search campaign is to research the different markets you’re entering to find which search engine or engines command the top shares.
Google is undoubtedly the leading search engine in the world, which means it commands the highest share globally, but not every country follows suit.
There are countries in the world in which advertising through Google AdWords won’t provide you the reach you need to successfully market your business.
I therefore recommended you look into the market share each search engine possesses in every country in which you plan to advertise.
Luckily, you will find this information, for Asia, throughout the following chapters.
Differences in Language
One thing to be careful of when running a global paid search campaign is the differences in character limits for each country.
In Asia, you have Japanese, Chinese, and Korean, which are 2-byte languages.
This means that 2 bytes are required to display one character.
English, on the other hand, needs only 1 byte.
This means that languages like Japanese or Chinese are allowed fewer characters for their PPC ads when compared to the 1 byte languages like English, because each character uses more data.
Language and Regional Settings at the Campaign Level
It is very important to set up your multilingual PPC campaigns effectively.
Google AdWords allows for campaign level language and regional settings to be made, so it is recommended you adjust according to your marketing situation.
You should first ask yourself the following questions:
- Should I target a specific region or country?
- Should I target a specific language?
These two questions are necessary to ask yourself when formulating a global PPC campaign.
When targeting foreign countries, such as Singapore or Hong Kong, for example, there can be multiple languages you need to consider.
In the case of multiple languages, such as in these two nations, you can create campaigns and landing pages for each target language.
Having both Chinese and English landing pages, along with their accompanying PPC campaign data in English and Chinese, will ensure more traffic reaches your site.
On the other hand, if you just want to target one specific language, you can choose the whole world as your targeted region and reach speakers of that language across the globe.
If you plan not to designate a specific service area, it is best to set the whole world as your advertising region.
1 Campaign, 1 Language Rule
When developing PPC campaigns, it is recommended you assign one language to each campaign.
When naming these campaigns, make sure to include the language and area so you can organize and operate them more effectively.
Example — Campaign naming:
- Hong Kong (English) Brand campaign = HK | EN | Brand
- Hong Kong (Chinese) Brand campaign = HK | CN | Brand
- Mexico (Spanish) Brand campaign = MX | ES | Brand
- Spain (Spanish) Brand campaign = ES | ES | Brand
The structure you develop for your multilingual campaigns will greatly affect their overall performance.
Constructing your account half-heartedly might lead to your not reaching the level of performance you were expecting, because the mere daily operation of your account will become an inefficient ordeal.
If you are operating a large paid search account, you might want to consider splitting it into multiple accounts based upon language.
This might end up being more convenient and effective, as you will be able to allocate and adjust your budgets better, and all the internal data will be unified by language.
Matters such as these are truly decisions you need to make on a case-by-case basis.
What is most important overall is to keep your campaigns’ structure identical or similar to your company’s website.
Fig 2.1: The language settings screen.
Ad Group Creation
As explained above, it is ideal to assign each campaign just one language.
Since ad groups are subsumed within campaigns, the same theory will apply to them.
Although it is possible to apply numerous languages to ad groups, each ad group should ideally have the same language as its campaign.
Ideal Keyword Lists
In order to maximize your paid search performance, it is also necessary to optimally format your keyword lists.
First and foremost, it is highly recommended you do not merely directly translate your English language keywords into the other languages in which you are marketing.
Sometimes, a translation of your keyword will be accurate in the literal sense, but it isn’t actually what is being searched for by users in the target language.
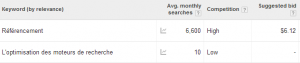
For example, if you were to translate the phrase “search engine optimization” into French, you would get “l’optimisation des moteurs de recherché.”
While this makes sense literally, the word “Référencement” is the actual term that is used.
Take a look at the following data, extracted using the AdWords Keyword Planner:
Fig 2.2: Simple translations do not allow you to find the proper keywords.
When generating your global keyword lists, you will also need to consider including variations of each keyword.
For example, there will be instances in which slang terms are searched for more than their dictionary entry counterparts.
Also, there can exist differences in search volume depending on location.
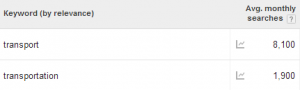
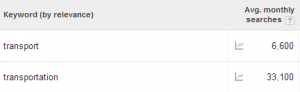
Taking the English language as an example, in America, “transportation” is the most searched term for finding different means of traveling from point A to point B, but in England, “transport” is preferred.
Fig 2.3: Search volumes for “transport” and “transportation” in England.
Fig 2.4: Search volumnes for “transport” and “transportation” in America.
Selecting the proper keywords for your different campaigns will ensure optimal performance.
I firmly recommend you have a native speaker of the variety of language you are targeting develop your keyword lists or you use a multilingual SEM expert with experience in the targeted languages.
The keyword lists that you upload into your account(s) are directly linked to the success of your PPC advertising campaigns.
If you do not ensure accuracy and optimal reach via native speakers, you can end up incurring unnecessary costs, which will decrease your overall performance.
Ad Copy Structure
PPC ads for your global campaigns need to be written by people with copywriting experience.
Words are limited in PPC ads, and there are competing advertisers to deal with, so you need to create ad copy that capture users’ attention and makes them want to learn more about your product or service.
Just by changing the way you use your words to convey a message, you can experience better results.
Let’s use an online shoe store as an example.
This store normally sells their shoes for $100, but currently they are running a campaign that has reduced it to $50:
- “Shoes Normally $100, Now Only $50!”
- “$100 Shoes, Now 50% Off!
Both ads say the same thing, but certain users will construe them differently.
In light of the above ads, the effect of a price can be more powerful than a percentage, or vice versa, depending on the country where you are advertising.
This type of issue is something you have to consider though, especially when copywriting in multiple languages.
For instance, areas other than price might be more effective to focus on, such as secure shipping, timely deliveries, or a flexible return policy.
The One Language Principle
When you run global paid search campaigns, it is highly recommended you unify your keywords, ads, and landing pages by using the same language.
If a landing page is in a different language from its ads and keywords, your overall performance will take a hit.
For instance, if a user clicks on an English language ad and is brought to a German language landing page, even if he is a speaker of both languages, he’ll probably question the legitimacy of the site and/or business.
Advertising in Different Locations
Google AdWords allows advertisers to segment their targets by language or regional settings.
The following items are the main criteria that Google uses to categorize different target segments:
-
Google domain display
If advertising in Japan using the Japanese language, ads will be shown on the domain www.google.co.jp.
Moreover, when the advertising language is set to Japanese, ads will be shown to users whose personal Google search settings are set to Japanese.
-
IP address
IP address information will also be referred to Google to designate a region.
For example, if you target Taiwanese consumers, search results will include users of www.google.com.tw as well as those who have a Taiwanese IP address and search on www.google.com.
-
Google account language
If a user possesses a Google account, he can set his main language for the account.
If the set language is English, ads that are in English will be shown to the user.
Let’s say an American hotel is trying to target users from Hong Kong and that both English and Chinese are used in the marketing campaign.
The advertising location is Hong Kong, and the advertisements are in English and Chinese.
While this would help extend one’s advertising reach within Hong Kong, it wouldn’t extend to Hong Kongese outside the country.
Thus, when Hong Kongese are traveling abroad, say in America, and using their smart devices to make hotel reservations in the U.S., they will be disregarded if Hong Kong is the only designated advertising location.
This shows you must consider all possibilities when designating your regional and language settings for your PPC campaigns.
Landing Page Settings
If you haven’t created a landing page in the specific language you want to advertise in, you naturally do not want to run ads for that language.
When developing or selecting landing pages, make sure they have corresponding ads in the same language that will guide users to them.
If they are different, you risk losing conversions to confused users.
PPC Advertising = Marketing Research
When a business wants to promote its products or services overseas, they often do not know what country is best to target.
For a case such as this, paid search can help you discover what locations will be most profitable.
By setting the advertising regions to “all” and language to “English”, users all around the world who search in English will be targeted.
After a while, you will gather enough data to generate informative reports via Google AdWords’ report feature, whereupon you can analyze the findings and discover which countries best meet your needs.
You then can decide whether or not to stop advertising in countries with higher than ideal cost per acquisition (CPA).
With real data, you will know which countries have the most demand for your products/services.
Of course, you can initially find out how many potential consumers can be reached by just referring to Google’s search volume data, but when it comes to the actual sales of your products/services, gathering real data on which countries are best is something that Google’s numbers cannot tell you.
Multilingual PPC advertising requires much research and preparation before you actually start running campaigns.
If you do it properly, though, and effectively operate your campaigns, PPC can be a very powerful advertising medium.
Don’t be afraid to fail, though, as trial and error is an important part of the paid search advertising process.
Basics of Multilingual SEO
There are three important points to remember about global SEO:
- Ensure proper regional targeting.
- Develop content strategies for each advertising language.
- Plan link-building strategies for each country in which you advertise.
Proper Regional Targeting
For multilingual SEO, properly setting your target regions is an important matter.
When performing SEO on a website with multiple languages, it is important to not only have a solid internal and external SEO strategy, you also need to properly target your advertising region; otherwise, your work will be pointless.
The search engines, Google and Bing, base their targeting on multiple information sources, some of which I will share with you in this section.
-
IP Address Information
Most search engines use websites’ hosting locations (IP address information) to classify their regional settings.
This means that for sites hosted in Mexico, Spanish content would be expected to be found on the site, while sites hosted in Italy would feature Italian content.
To use Italy as an example, this means hosting a site in Italy is the best choice for Italian SEO.
However, when marketing globally, the location of a business office and the location of its hosting site are probably in completely different areas.
If a business has a global site, it would be difficult to have different hosting servers for each language, so it is ultimately unrealistic to think search engines only designate a site’s location based on where it’s hosted.
If you think about this issue from the perspective of a user, a business hosting its site in the same country will help to increase its access speed (countries with poor internet infrastructure excluded).
As such, search engines do not use only this piece of information for determining location.
In reality, search engines choose to refer to multiple pieces of information to determine the target region of a website.
-
Country Code Top Level Domain
Country code top level domain (ccTLD) is a rather influential factor for search engines in determining a website’s target region.
The ccTLD is indicated by the letters appearing to the right of a URL: for example, “fr” is the ccTLD in www.yourdomain.fr.
The “fr” indicates that it is a French website, and the “sg” in www.yourdomain.sg shows it is a Singaporean site.
Of course, if the URL is www.yourdomain.sg, we can expect that its owners are targeting Singapore.
Thus, with a ccTLD, it is easy to designate a region, and search engines use it as a clear indicator for their targeting.
However, a ccTLD cannot tell whether the website’s owner is incorporated or conducting business in the same country.
Regarding using ccTLDs from the perspective of SEO, it is best to consider it on a case-by-case basis.
The problem with acquiring a new ccTLD domain is that there are no backlinks directed toward it.
When you acquire a new domain, you can naturally expect that it will take time to move up in the SERPs without a history of backlinks.
Also, while a ccTLD does help to designate a region, it doesn’t seem to have a direct connection to helping improve your ranking.
(Search engines have stated that ccTLDs aren’t considered in terms of ranking).
With regard to areas other than SEO, ccTLDs do have their merits.
For example, a ccTLD gives visitors a sense of trust, as it is an indicator that the business is local.
It’s probably safe to say most consumers are more comfortable purchasing items from a site in their own country than a site located in a foreign one.
Overall, it is up to you to consider whether acquiring a new ccTLD is beneficial or not.
| Generic top level domain (gLTD) | .com, .net, .org, .biz, .info, etc. |
| Country code top level domain (ccTLD) | .jp (Japan), .de (Germany), .fr (France), .tw (Taiwan) |
-
Website Language and Content
Search engines use the language and content of a website as one piece of information in classifying its location.
For example, the Russian search engine, Yandex, indexes pages in Russian and English, but Japanese or Chinese pages are not indexed much at all.
Information, such as phone numbers or addresses, is also used to determine target region; these items are weak indicators though.
Also, you can determine the country or region of a page just by the language in which it is written.
-
Google Webmaster Tools for Regional Targeting
Google’s Webmaster Tools allows users to easily perform regional targeting for their website.
This feature also allows regional targeting for cases in which the folders or subdomains of a single website are isolated by language.
While this feature is normally convenient, it can only be used with generic domains, such as .com, .org, .net, etc.
-
Regional targeting with Meta Tags
It is also possible to use meta tags to designate location.
Currently, Google does not use meta tags for distinguishing a site’s region, but for other search engines, like Microsoft’s Bing, which does not have a regional targeting feature, it is possible.
<meta http-equiv=”content-language” content=”XX”>
| Code | Language |
| BG | Bulgarian |
| CS | Czech |
| DA | Danish |
| DE | German |
| EL | Greek |
| EN | English |
| EN-GB | English-Great Britain |
| EN-US | English-United States |
| ES | Spanish |
| ES-ES | Spanish-Spain |
| FI | Finnish |
| FR | French |
| FR-CA | French-Quebec |
| FR-FR | French-France |
| HR | Croatian |
| IT | Italian |
| JA | Japanese |
| KO | Korean |
| NL | Dutch |
| NO | Norwegian |
| PL | Polish |
| PT | Portuguese |
| RU | Russian |
| SV | Swedish |
| ZH | Chinese |
Search engines use various forms of information, as outlined above, to perform their location targeting.
Since each search engine has its own unique indicators for targeting, it is not certain which indicators are the most influential.
Therefore, you will need to perform your SEO in light of each search engine’s own targeting variables.
Separating Site Maps by Language
Currently, site maps are supported by many search engines.
By setting your site map, you can identify search engine crawling errors, so this is a great feature for SEO.
If your content is displayed in many languages, you can make site maps for each language, such as:
- http://www.example.com/VN/xml
- http://www.example.com/JP/xml
- http://www.example.com/UK/xml
Multilingual Content Strategies
It is crucial that you have a well-developed content strategy for your global SEO.
Just focusing on the technical aspects of SEO is not enough to be successful on the worldwide stage.
Though many individuals look to extensive link building measures for their SEO, as it was successful in the past, many companies have shifted their focus to quality content.
When creating content for your SEO, you’ll need to consider how best to insert your target keywords on top of producing quality content.
For global SEO, since you will be dealing with multiple languages, mere translations of your original text will not suffice.
Help from people with multilingual SEO content writing experience is recommended.
What is important overall is that you research what level of content you will need for SEO in different languages and make sure to have native speakers write it for you.
If this is difficult to do in-house, outsourcing is a viable alternative.
Beware of Duplicate Content
For multilingual SEO, sometimes people target multiple locations with one language.
A good example of this is targeting the United Kingdom and America using the English language.
English is pretty much the same worldwide, save for differences in vocabulary, pronunciation, and colloquial phrasing, so you would think it was OK to use the same content worldwide.
This is not a good idea, though, as it can lead to the possibility of search engines penalizing you for duplicate content, which can actually lead to your being removed from search engine indices.
It is recommended that you change content for each target region, even if it is the same language, because there is always the possibility of being removed from a search engine’s index.
Regional Link Building
SEO on search engines other than Google (Baidu, Yandex, Bing, etc.) also requires strategic link building.
For countries that still have underdeveloped SEM industries, you can expect that there are fewer businesses doing SEO, and, thus, it will be easier for you to rank higher in the SERPs.
This is changing each year, though, so it is important to develop a solid strategy early on.
Multilingual link building strategies involve getting links from sites all in the same language.
While in the past, it was possible to increase your Chinese SERP rank via English language site backlinks containing Chinese keywords, this has changed.
Now these types of links are considered spam.
Handling Google
Currently, Google is the most used search engine in the world. This means that for global SEM, you will have to perform SEO in light of Google in most cases.
Google fundamentally seems to handle the world’s myriad languages in the same fashion, but, of course, there are certain algorithms that need to be implemented in order to process languages that are different from English.
In terms of ranking, though, Google seems to treat variables in the same way even across borders. For example, if you consider how Google handles backlinks, results seem to be the same in Japan, America, Vietnam, Germany, or pretty much anywhere Google is accessed.
Google’s algorithm updates start in America (in the English language), so Penguin and Panda will be felt first in the U.S. and then in other locations across the globe.
This means that there is a time delay between the initial update in English and the subsequent updates in other languages.
It is therefore possible for certain non-English SEOs to foresee what changes will come and develop a strategy to handle it.
SEO for Bing
SEO for Bing seems to mirror that of Google, meaning things like site content and backlinks are treated in the same manner.
It is difficult to measure the differences, though, as there is not much information on Bing available in the SEO industry due to its smaller share of the market.
However, this might be changing, at least for the Asia-Pacific region, as Yahoo Taiwan and Hong Kong both have replaced their search engines with Bing.
This has given the search engine a more influential role in the area. Here I will provide some general guidelines for SEO on Bing:
-
CTR is important
Bing appears to value the CTR of sites when ranking. This means the more a site is clicked, the better chance it has at moving up in the SERPs.
What is recommended then, is making sure your site’s meta data that appears in the SERPs, such as your title and description tags, do not just contain target keywords, but also effective copywriting that attracts more users to click on your site.
-
Bing Webmaster Tools
Bing has its own unique version of Webmaster Tools that you can take advantage of.
Using Bing Webmaster Tools, you will be able to get useful information for your site’s SEO, such as how to apply for URL indexation, sitemap settings, number of indexes, etc.
You can find Bing’s Webmaster Tools program via the following link:
- http://www.bing.com/toolbox/webmaster/
-
Content really matters
Since Google’s last update, websites with especially poor content or overall poor usability have been removed from Google’s index at a higher rate than before.
However, this trend is not limited to Google; it is also occurring on other search engines like Bing.
That’s why it is imperative you not only go about your link building strategies in the proper manner, but also produce high quality content if you want to succeed at global SEO.
Different Countries, Different SEO Challenges
The level of difficulty for SEO can change drastically from country to country. For example, in South Korea, where Naver is the main search engine, SEO is not even worth the effort as only three sites appear in the first page of organic results.
For other countries’ search engines though, such as Russia’s Yandex, there are existing link building markets.
In these countries, links are still an important part of SEO. In this respect, for different search engines, there are different SEO strategies that you have to implement.
For Asia, which isn’t dominated by Google as the rest of the world is, it is imperative you gain an understanding of the different search engines that are in use and how to perform SEO on them, if you wish to market successfully online in the region.
Still not sure how to successfully enter other markets with your business? Contact Info Cubic today and we’ll put you in touch with one of our multilingual marketing experts.